Overview
In this article we are going to show you how to allow STM32WB-based IoT device to communicate with ThingsBoard-driven UI application via Satellite communication and LoRa radio.
 Daniel Smyk
Daniel Smyk
 Daniel Smyk
Daniel Smyk
In this article we are going to show you how to allow STM32WB-based IoT device to communicate with ThingsBoard-driven UI application via Satellite communication and LoRa radio.

The rise of satellite-based IoT solutions has unlocked exciting new possibilities for businesses and developers, allowing them to connect devices even in the most remote areas. Lacuna Space is at the forefront of this innovation, offering global IoT connectivity through Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites and the highly efficient LoRaWAN communication protocol. Whether you're tracking environmental data in remote regions, monitoring assets at sea, or managing sensors in hard-to-reach places, Lacuna Space’s satellite network ensures your IoT devices stay connected where traditional networks fall short.
Lacuna Space operates a constellation of LEO satellites positioned between 300 and 1,500 kilometers above Earth. These satellites move swiftly across the sky, providing frequent coverage of any location due to their lower altitude. This setup significantly reduces signal latency compared to traditional geostationary satellites, which orbit at approximately 35,786 kilometers, enabling more responsive, real-time data transmission.
Unlike conventional satellite systems that rely on ground-based relay stations, Lacuna Space offers direct communication between IoT devices and satellites, cutting out intermediaries. This direct link not only reduces latency but also lowers operational costs. Devices equipped with LoRaWAN modules transmit small packets of data asynchronously, which are collected and buffered by the satellites. These packets are then forwarded to ground stations when the satellites pass overhead, where they are sent to cloud platforms for processing and analysis.
The Things Network (TTN) is a global, decentralized platform that enables the Internet of Things (IoT) through LoRaWAN technology. Driven by a community of developers, businesses, and hobbyists, TTN provides an open ecosystem where anyone can build and deploy IoT solutions without relying on expensive cellular or Wi-Fi networks. Its primary goal is to create a free and public IoT network that anyone can contribute to and use.
TTN is built on a layered architecture that includes:
Anyone can join the network by deploying a LoRaWAN gateway, helping expand global coverage. Local communities, known as TTN Chapters, work to organize and promote the network in their regions. These chapters are made up of individuals, businesses, and organizations that contribute to and benefit from the open IoT network.
By allowing broad participation, TTN creates a truly decentralized infrastructure.
ThingsBoard is an open-source platform designed to simplify the development, management, and visualization of IoT applications. As industries increasingly adopt IoT solutions to improve operational efficiency and make data-driven decisions, ThingsBoard provides a robust framework suited to a wide range of use cases—from smart cities to industrial automation.
At its core, ThingsBoard offers an intuitive environment for managing devices, allowing users to easily register and monitor large numbers of IoT devices. With remote device provisioning and configuration, along with over-the-air updates, devices can be maintained and upgraded without the need for physical access. This level of flexibility is particularly valuable in large-scale deployments where manual management would be impractical.
ThingsBoard supports multiple integrations, including MQTT, HTTP, Azure, Tuya, and TTN. After configuring an uplink decoder and setting up connection parameters, data can be automatically transferred from these integrations to ThingsBoard, enabling real-time data ingestion from connected devices.
One of ThingsBoard’s standout features is its customizable dashboards, which display both real-time and historical data through interactive charts, graphs, and maps. Users can design these dashboards to highlight key performance indicators and system health metrics, making it easy to assess operations and make informed decisions quickly. The user-friendly interface ensures that both technical and non-technical users can effectively engage with the data.
In addition to device management and data visualization, ThingsBoard offers powerful alerting and notification capabilities. Users can configure alerts based on specific conditions, ensuring that critical events trigger timely responses. Notifications can be sent via various channels, such as email or SMS, enhancing situational awareness and enabling quick interventions when needed.
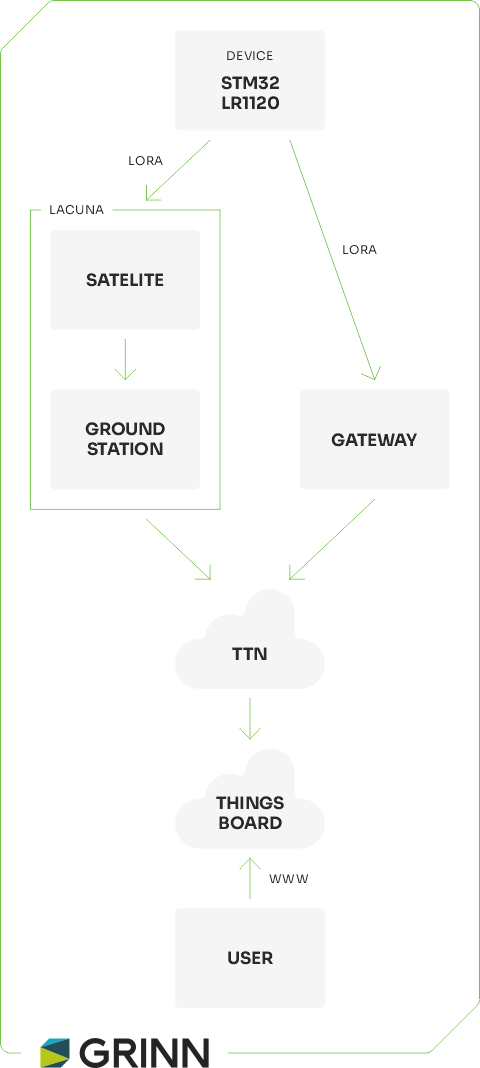
Our objective is to run the library provided by Lacuna Space on the STM32WB55 microcontroller alongside the LR1120 transceiver to send data to the satellite and display it on ThingsBoard. The device is capable of satellite communication using Lacuna Space libraries and satellites, as well as traditional terrestrial LoRaWAN communication through LoRa gateways.
In the satellite approach, data is transmitted to a satellite, which then forwards it to a ground station before being sent to The Things Network (TTN). In contrast, with the terrestrial approach, data goes directly from the gateway to TTN.
While the satellite approach is typically limited to one data frame per day, it offers a crucial advantage—allowing communication with devices in areas lacking LoRaWAN infrastructure or GSM coverage.
The STM32WB55 is a dual-core microcontroller from STMicroelectronics, designed specifically for wireless IoT applications. It combines an ARM Cortex-M4 processor for application code with an ARM Cortex-M0+ core dedicated to managing the Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) radio, making it ideal for low-power, wireless communication in IoT environments. With features such as enhanced security, power efficiency, and multi-protocol support, the STM32WB55 is fully compatible with Zephyr OS. This compatibility enables developers to manage tasks, drivers, and peripherals within a real-time environment, simplifying multitasking and efficient resource usage in embedded applications.
In our specific application with the STM32WB55, we leverage several key hardware interfaces to connect various peripherals and sensors:
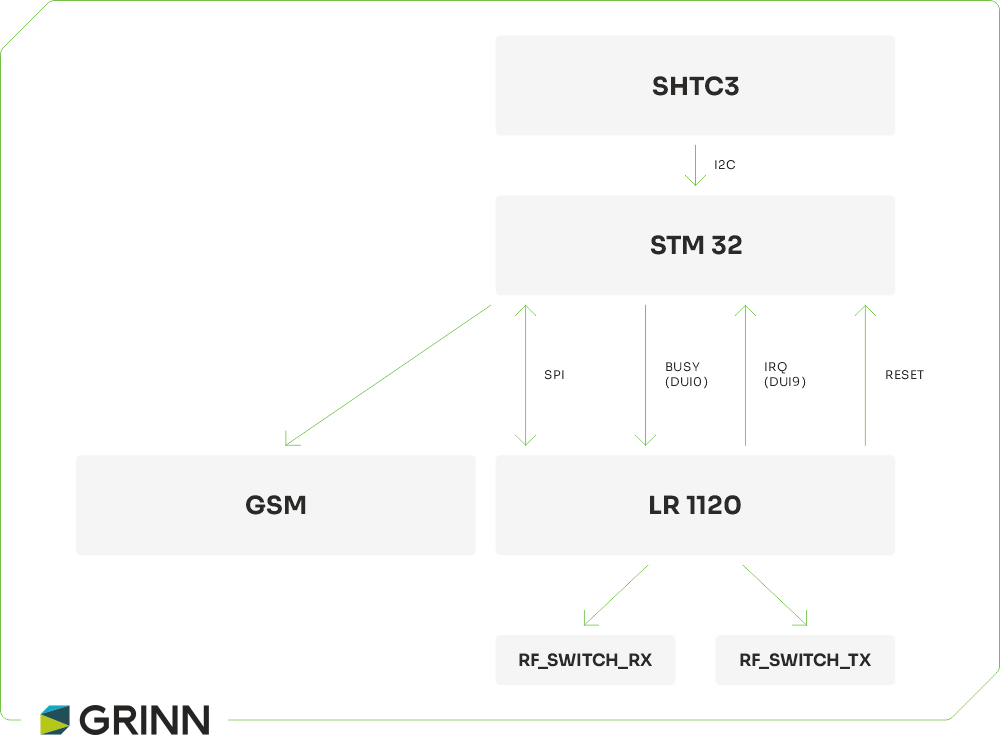
The LR1120 is a versatile transceiver chipset from Semtech that supports a wide range of frequencies and communication protocols, making it ideal for both terrestrial LoRaWAN gateways and satellite communications. Designed for long-range, low-power applications, the LR1120 enables devices to communicate across multiple bands, including sub-GHz and 2.4 GHz frequencies.
The LR1120 communicates with the host microcontroller via SPI and additional control pins, such as:
One of the LR1120’s key features is its integrated balun (balanced-to-unbalanced transformer), which simplifies antenna matching and impedance conversion. When designing your PCB, it's crucial to manage the antenna directionality using the appropriate control pins (DIO5 to DIO8, and DIO10) to optimize transmission and reception. The LR1120 manages these operations through designated control pins, ensuring efficient radio performance for both terrestrial and satellite communication links.
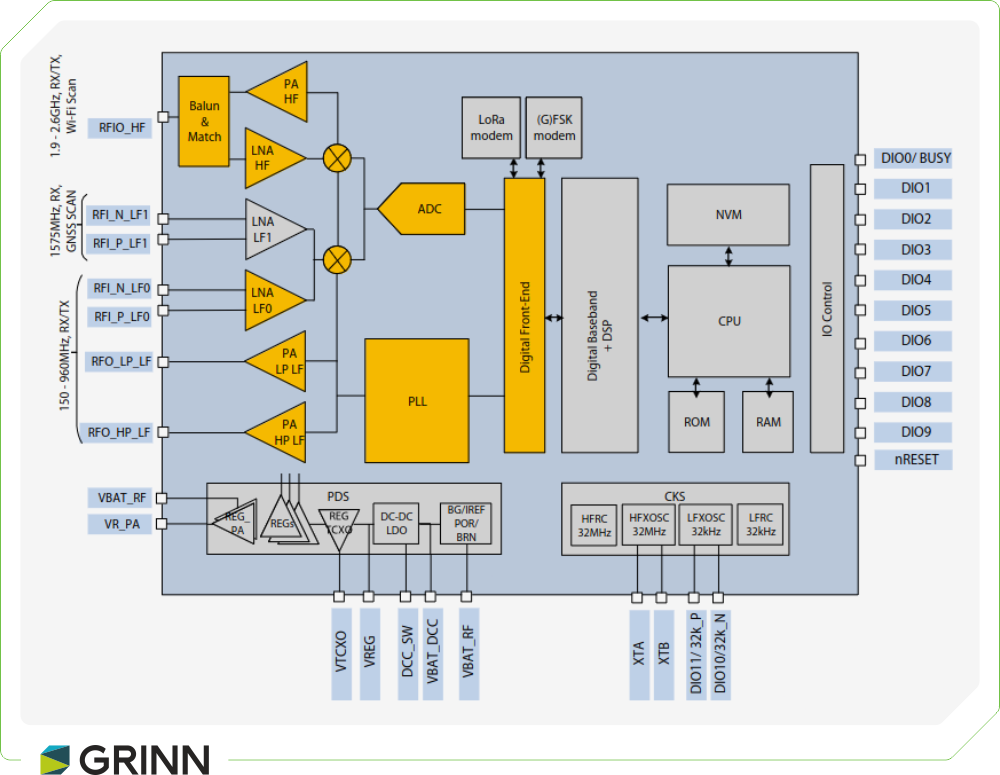 LR1120 block diagram. [https://semtech.my.salesforce.com/sfc/p/#E0000000JelG/a/RQ000001Dmkb/u.4kgx5bdN5SnZaf3pgDPCm531cEG5ILp9oX_yejcNg]
LR1120 block diagram. [https://semtech.my.salesforce.com/sfc/p/#E0000000JelG/a/RQ000001Dmkb/u.4kgx5bdN5SnZaf3pgDPCm531cEG5ILp9oX_yejcNg]
Lacuna Soft Modem
Lacuna Space provides two versions of an object library written in C++ to help users leverage their satellite IoT technology. The first version, called Lacuna Soft Modem, is designed for Arduino and includes examples of using the library to communicate with a satellite. The second, Lacuna Soft Modem Portable, offers greater flexibility, allowing for custom implementations of key classes.
Both libraries are available on the Lacuna Dashboard, which also provides tools for checking upcoming satellite passes and registering devices on the Lacuna Satellite Network Service. To access these features, you’ll need to create a Lacuna account using your email address. Currently, access to these resources is limited to participants in the Lacuna Technology Partner Program.
Lacuna also hosts a developer forum, where developers can ask support questions and share knowledge with others in the community.
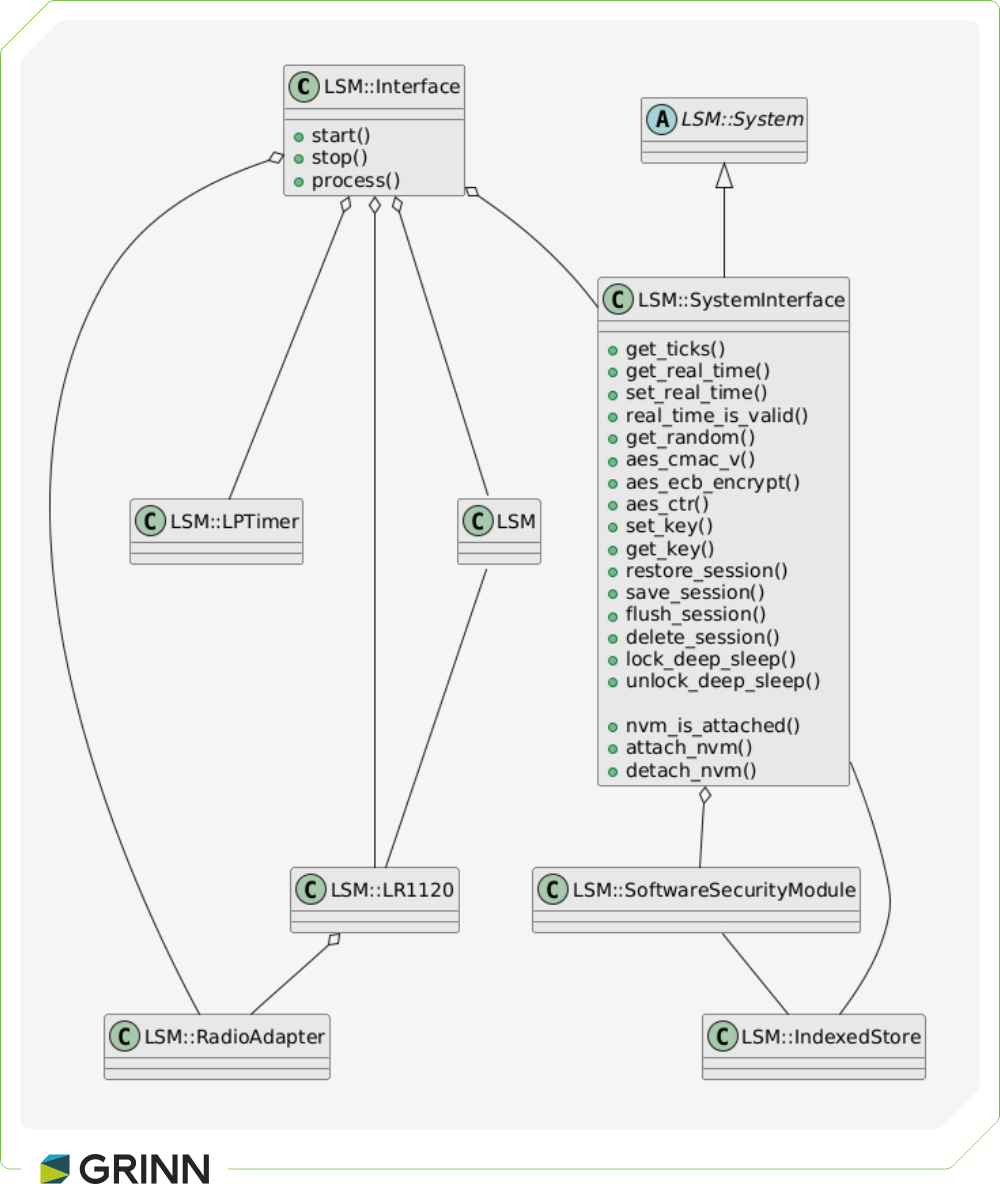 Lacuna Soft Modem api architecture
Lacuna Soft Modem api architecture
The minimum required components are organized within LSM::LR1120Interface. Subclasses of LSM::System handle essential tasks, such as:
Lacuna Space Almanac
The almanac is a critical component in Lacuna Space’s satellite IoT system, providing essential information about satellite positions and timing. It enables your IoT device to predict when a satellite will be overhead and ready for communication.
Purpose of the Almanac
The almanac contains orbital data that helps your device calculate the position of satellites relative to its location on Earth. This timing is crucial because satellite passes vary depending on your device’s position and the satellite’s orbit. By keeping the almanac up to date, your device can "wake up" at the right moment to transmit data, rather than continuously scanning for satellites and wasting power.
Importance of Maintaining an Updated Almanac
The almanac has a limited validity period and needs to be regularly updated. If the almanac becomes outdated, your device won’t know when the next satellite pass will occur, forcing it to stay in constant RX mode (receive mode) to wait for an updated almanac from a satellite. This constant listening consumes significant power, reducing your device’s battery life. Regular updates ensure efficient, low-power operation.
How to Access the Almanac
You can download the latest almanac from Lacuna Space’s official website. It’s recommended to check the Lacuna Space dashboard for updates or wait for your device to receive it directly from a satellite. Below is a screenshot of where you can find the almanac on the website:
 LacunaSpace Almanac page
LacunaSpace Almanac page
More in Part 2. Coming soon.

Daniel is an Embedded Software Developer at Grinn, contributing to firmware development, system integration, and the delivery of robust embedded solutions.
Daniel is an Embedded Software Developer at Grinn, contributing to firmware development, system integration, and the delivery of robust embedded solutions.

Grinn is now a Bluetooth® SIG member, learn more about how you as a client will benefit from it. The Bluetooth® Special Interest Group is a community of innovators of Bluetooth® technology. Since Grinn actively uses Bluetooth® wireless technology in its projects, it is important for us to get the latest knowledge from the original source and apply it when developing new products.

When talking about IoT, often the most expensive component is embedded software development. Let's talk about how you can save on development without compromising quality.

Welcome all candidates and future employees of Grinn! In this article, you will learn all about how our recruitment process works and how you can better prepare for your interview. At Grinn we specialize in IoT solutions, IoT device design, embedded software development, electronic design, and mechanical engineering tasks.
What did our clients say?
Clients value our can-do approach and practical way to solve a problem.






Clients say Grinn is like a direct part of their company.








Clients highlight that we are professionals and working with us guarantees quality.






We offer a complete package of everything needed to create world-class hardware products, from design to production.




Always on time and always ready to listen to new input and pivot if required.


Clients say we don't only make the hardware, but trully put in the effort to understand the problem you are trying to solve and proactively think along side with you.











Your message
was sent!
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get in touch as soon as possible!
Your message
was sent!
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get in touch as soon as possible!
Your message
was sent!
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get in touch as soon as possible!